Introduction:
RF radio testing is the process of measuring the energy of electromagnetic fields propagating in the living environment, we can use receiving antennas and receivers in the laboratory with the use and capture the power of these radio signals, this test is called EMC testing; we can also utilize radio RF testing in real-life applications to provide productivity and improve the human living environment.
Introduction to RF Radiation:
RF stands for Radio Frequency, RF is any frequency in the electromagnetic spectrum associated with the propagation of radio waves, when RF current is supplied to an antenna it creates an electromagnetic field which is subsequently able to propagate through space, many wireless technologies are based on RF field propagation, these frequencies form part of the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation.
Electromagnetic radiation consists of waves of electrical and magnetic energy that move (i.e. radiate) together through space at the speed of light. In summary, all forms of electromagnetic energy are referred to as the electromagnetic spectrum; radio waves and microwaves emitted by transmitting antennas are a form of electromagnetic energy, and the term electromagnetic field or radio frequency (RF) field is commonly used to refer to the presence of electromagnetic or RF energy.
RF fields have both electric and magnetic components (electric and magnetic fields). It is often convenient to express the strength of the RF environment at a given location in units specific to each component, e.g., the unit "volts per meter" (V/m) is used to measure the strength of the electric field, and the unit "amperes per meter" (A/m) is used to express the strength of the magnetic field.
Radio Spectrum Division:
RF waves can be characterized by a wavelength λ and a frequency f. The wavelength λ is the distance covered by a complete cycle of an electromagnetic wave, λ = C/f, C being the speed of light. Meanwhile, the frequency is the number of electromagnetic waves per unit of time passing through a given point.RF signal frequency is usually expressed in units called hertz (Hz), with 1 Hz equaling one cycle per second, one megahertz (MHz) equaling one million cycles per second, and one gigahertz (GHz) equaling one billion cycles per second, or one thousand megahertz.
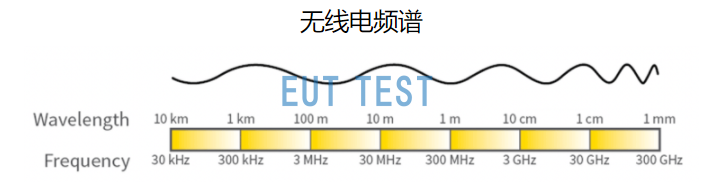
Wavelength of the radio spectrum at different frequencies
RF testing in real-life applications:
RF energy is integrated in a wide variety of applications from telecommunications to non-communications applications and for medical purposes, with telecommunications being perhaps the most prevalent and widely used form of this energy.
Telecommunications applications:
We can find it in radio and television broadcasts, police and fire department radio communications, amateur radio, microwave point-to-point links, cellular equipment and satellite communications.
Our daily life can be accessed in the wireless wifi, bluetooth, cell phones, etc. are typical of the use of radio frequency testing.
Applications in the medical field:
In more specific applications, such as in the medical field, RF energy serves the same designated purpose.MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) uses RF waves to generate images of the human body. RF is also used to destroy cancer cells and for cosmetic treatments to tighten skin, reduce fat or promote skin cell healing.
Radio Frequency Testing for Medical Purposes in Real Life Applications - MRI
Other applications:
- Other non-communication applications that use RF energy are things like microwave ovens, where RF energy is used to heat food.
- In addition, RF energy can be used for industrial heating and sealing. Industrial heaters and sealers generate RF radiation that rapidly heats the material being processed in the same way that microwave ovens cook food.
- RF energy is also used in industrial applications such as molding plastic materials, gluing wood products, sealing items (e.g., shoes and purses), and processing food.
- Other industrial applications include the testing of RF components and the measurement of material density.
- Radar is another valuable tool for using RF energy and is widely used in areas such as traffic enforcement, air traffic control, weather monitoring and military applications.
Focus on the impact of RF:
Due to the large number of RF applications worldwide, electronic products and systems in life must operate in their electromagnetic environment and must not emit electromagnetic interference to the outside. Therefore, RF immunity and emission testing must be performed on a product or system before it is released to the market. In order to perform RF immunity testing, a device is exposed to RF interference and magnetic fields and exhibits a certain field strength and frequency range in its operating environment. When testing a piece of equipment for RF emissions, under normal operation, the equipment is monitored for RF interference and magnetic fields.
If you want to understand more about EMC testing, please read:About the concept of EMC electromagnetic compatibility and EMC test system introduction

